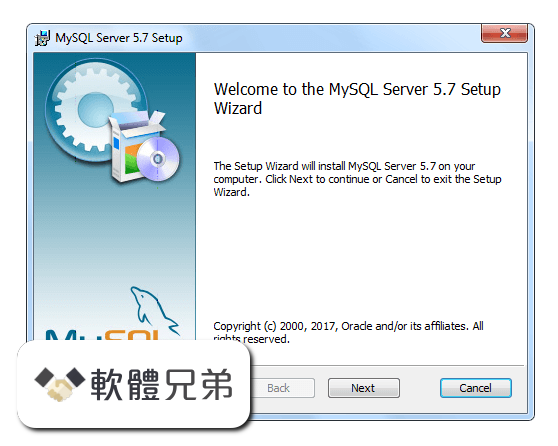
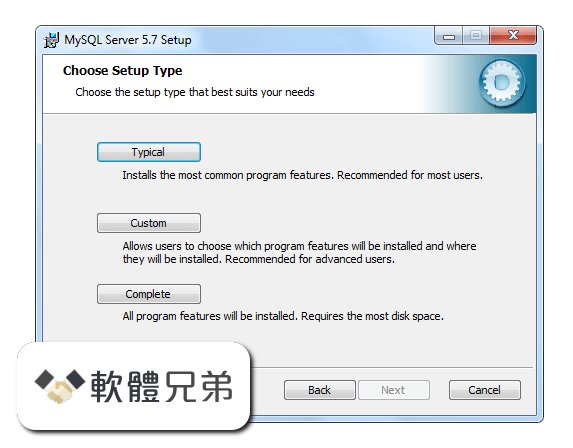
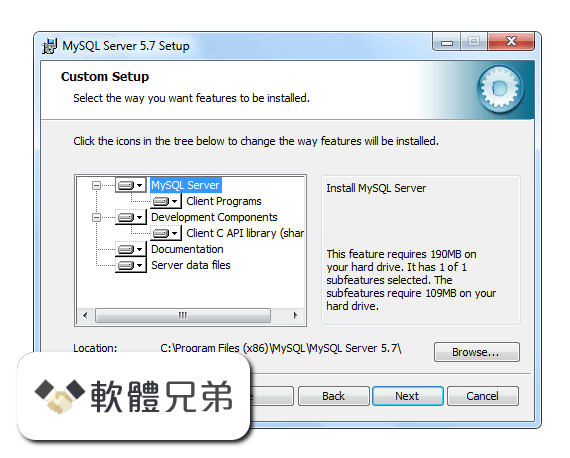
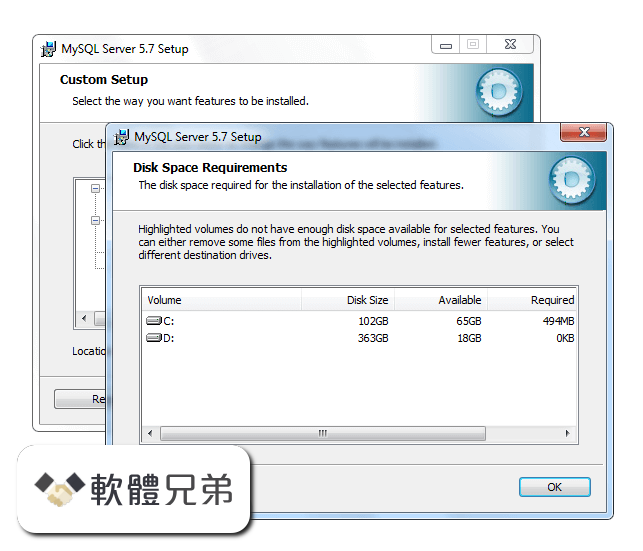
|
What's new in this version: * Important Change: Replication: RESET MASTER and RESET SLAVE now reset the values shown for Last_IO_Error, Last_IO_Errno, Last_SQL_Error, and Last_SQL_Errno in the output of SHOW SLAVE STATUS. (Bug#44270)
See also Bug#34654.
Bugs fixed:
* Partitioning: Security Fix: Accessing a table having user-defined partitioning when the server SQL mode included ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY caused the MySQL server to crash. For example, the following sequence of statements crashed the server:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS t1;
SET SESSION SQL_MODE='ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY';
CREATE TABLE t1 (id INT, KEY(id))
PARTITION BY HASH(id) PARTITIONS 2;
(Bug#45807)
* Important Change: Replication: When using STATEMENT or MIXED binary logging format, a statement that changes both non-transactional and transactional tables must be written to the binary log whenever there are changes to non-transactional tables. This means that the statement goes into the binary log even when the changes to the transactional tables fail. In particular, in the event of a failure such statement is annotated with the error number and wrapped inside a pair of BEGIN and ROLLBACK statements.
On the slave, while applying the statement, it is expected that the same failure and the rollback prevent the transactional changes from persisting. However, statements that fail due to concurrency issues such as deadlocks and timeouts are logged in the same way, causing the slave to stop since the statements are applied sequentially by the SQL thread.
To address this issue, we ignore concurrency failures on the slave. Specifically, the following failures are now ignored: ER_LOCK_WAIT_TIMEOUT, ER_LOCK_DEADLOCK, and ER_XA_RBDEADLOCK. (Bug#44581)
* Partitioning: Truncating a partitioned MyISAM table did not reset the AUTO_INCREMENT value. (Bug#35111)
* Replication: The SHOW SLAVE STATUS connection thread competed with the slave SQL thread for use of the error message buffer. As a result, the connection thread sometimes received incomplete messages. This issue was uncovered with valgrind when message strings were passed without NULL terminators, causing the error Conditional jump or move depends on uninitialised value(s). (Bug#45511)
See also Bug#43076.
* Replication: Large transactions and statements could corrupt the binary log if the size of the cache (as set by max_binlog_cache_size) was not large enough to store the changes.
Now, for transactions that do not fit into the cache, the statement is not logged, and the statement generates an error instead.
For non-transactional changes that do not fit into the cache, the statement is also not logged — an incident event is logged after committing or rolling back any pending transaction, and the statement then raises an error.
Note
If a failure occurs before the incident event is written the binary log, the slave does not stop, and the master does not report any errors.
(Bug#43929)
See also Bug#37148.
* Replication: The --database option for mysqlbinlog was ignored when using the row-based logging format. (Bug#42941)
* Replication: Shutting down the server while executing FLUSH LOGS, CHANGE MASTER TO, or STOP SLAVE could sometimes cause mysqld to crash. (Bug#38240)
* Replication: When reading a binary log that was in use by a master or that had not been properly closed (possibly due to a crash), the following message was printed: Warning: this binlog was not closed properly. Most probably mysqld crashed writing it. This message did not take into account the possibility that the file was merely in use by the master, which caused some users concern who were not aware that this could happen.
To make this clear, the original message has been replaced with Warning: this binlog is either is use or was not closed properly. (Bug#34687)
* The server crashed if evaluation of GROUP_CONCAT(... ORDER BY) required allocation of a sort buffer but allocation failed. (Bug#46080)
* When creating tables using the IBMDB2I storage engine with the ibmdb2i_create_index_option option set to 1, creating an IBMDB2I table with a primary key should produce an additional index that uses EBCDIC hexadecimal sorting, but this index was not created. (Bug#45983)
* With InnoDB tables, MySQL used a less-selective secondary index to avoid a filesort even if a prefix of the primary key was much more selective.
The fix for this problem might cause other queries to run more slowly. (Bug#45828)
* The server crashed for attempts to use REPLACE or INSERT ... ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE with a view defined using a join. (Bug#45806)
* Some collations were causing IBMDB2I to report inaccurate key range estimations to the optimizer for LIKE clauses that select substrings. This can be seen by running EXPLAIN. This problem primarily affects multi-byte and unicode character sets. (Bug#45803)
* Invalid memory reads and writes were generated when altering merge and base tables. This could lead to a crash or Valgrind errors:
==28038== Invalid write of size 1
at: memset (mc_replace_strmem.c:479)
by: myrg_attach_children (myrg_open.c:433)
by: ha_myisammrg::attach_children() (ha_myisammrg.cc:546)
by: ha_myisammrg::extra(ha_extra_function) (ha_myisammrg.cc:944)
by: attach_merge_children(TABLE_LIST*) (sql_base.cc:4147)
by: open_tables(THD*, TABLE_LIST**, unsigned*, unsigned) (sql_base.cc:4709)
by: open_and_lock_tables_derived(THD*, TABLE_LIST*, bool) (sql_base.cc:4977)
by: open_n_lock_single_table (mysql_priv.h:1550)
by: mysql_alter_table(sql_table.cc:6428)
by: mysql_execute_command(THD*) (sql_parse.cc:2860)
by: mysql_parse(THD*, char const*, unsigned, char const**) (sql_parse.cc:5933)
by: dispatch_command (sql_parse.cc:1213)
(Bug#45796)
* Inserting data into a table using the macce character set with the IBMDB2I storage engine would fail. (Bug#45793)
* There was a race condition when changing innodb_commit_concurrency at runtime to the value DEFAULT. (Bug#45749)
See also Bug#42101.
* Performing an empty XA transaction caused the server to crash for the next XA transaction. (Bug#45548)
* For replication of a stored procedure that uses the gbk character set, the result on the master and slave differed. (Bug#45485)
* SHOW CREATE TRIGGER requires the TRIGGER privilege but was not checking privileges. (Bug#45412)
* An assertion failure could occur if InnoDB tried to unlock a record when the clustered index record was unknown. (Bug#45357)
* Bug#19027 caused --enable-plugin_name (for example, --enable-innodb) not to work. (Bug#45336)
* If autocommit was enabled, InnoDB did not roll back DELETE or UPDATE statements if the statement was killed. (Bug#45309)
* Use of DECIMAL constants with more than 65 digits in CREATE TABLE ... SELECT statements led to spurious errors or assertion failures. (Bug#45262)
* The mysql client could misinterpret some character sequences as commands under some circumstances. (Bug#45236)
* Use of CONVERT() with an empty SET value could cause an assertion failure.
(Bug#45168)
* InnoDB recovery could hang due to redo logging of doublewrite buffer pages. (Bug#45097)
* when reading binary data, the concatenation function for geometry data collections did not rigorously check for available data, leading to invalid reads and server crashes. (Bug#44684)
* If an error occurred during the creation of a table (for example, the table already existed) having an AUTO_INCREMENT column and a BEFORE trigger that used the INSERT ... SELECT construct, an internal flag was not reset properly. This led to a crash the next time that the table was opened again. (Bug#44653)
* For queries with a sufficient number of subqueries in the FROM clause of this form:
SELECT * FROM (SELECT 1) AS t1,
(SELECT 2) AS t2,
(SELECT 3) AS t3, ...
The query failed with a Too high level of nesting for select error, as those the query had this form:
SELECT * FROM (SELECT 1 FROM (SELECT 2 FROM (SELECT 3 FROM ...
(Bug#44156)
* configure.in contained references to literal instances of nm and libc, rather than to variables parameterized for the proper values on the current platform. (Bug#42721)
* configure.in did not properly check for the pthread_setschedprio() function. (Bug#42599)
* A workaround for a Sun Studio bug was instituted. (Bug#41710)
* Valgrind warnings that occurred for SHOW TABLE STATUS with InnoDB tables were silenced. (Bug#38479)
* In the mysql client, if the server connection was lost during repeated status commands, the client would fail to detect this and command output would be inconsistent. (Bug#37274)
* When invoked to start multiple server instances, mysqld_multi sometimes would fail to start them all due to not changing location into the base directory for each instance. (Bug#36654)
* Renaming a column that appeared in a foreign key definition did not update the foreign key definition with the new column name. (Bug#21704)
MySQL 5.1.37 相關參考資料
Central Repository: mysqlmysql-connector-java5.1.37
mysql/mysql-connector-java/5.1.37 ../ COPYING 2015-10-06 15:24 18122 COPYING.asc 2015-10-06 15:24 232 COPYING.md5 2015-10-06 15:24 33 COPYING.sha1 ...
https://repo.maven.apache.org
Download MySQL Community Server (Archived Versions)
5.1.37, 5.1.36, 5.1.35, 5.1.34, 5.1.33, 5.1.32, 5.1.31, 5.1.30, 5.1.5a alpha, 5.0.96, 5.0.95, 5.0.92, 5.0.91, 5.0.90, 5.0.89, 5.0.88, 5.0.87, 5.0.86, 5.0.85 ...
https://downloads.mysql.com
Download MySQL Community Server 5.1.37 for Windows
MySQL Community Server 5.1.37 · File Size: 35.73 MB · Date Released: Add info · Works on: Windows 2000 / Windows 7 / Windows 8 / Windows 98 / Windows Vista / ...
http://www.oldversion.com
jdbc连接mysql驱动包(mysq-connector-java-5.1.37和 ...
2021年3月24日 — jdbc连接mysql驱动包(mysq-connector-java-5.1.37和mysq-connector-java-8.0.12) 转载 ... 百度链接中提供两个mysql驱动包,mysql数据库版本8.0以上的用第 ...
https://blog.csdn.net
MySQL ConnectorJ - (Archived Versions)
5.1.37, 5.1.36, 5.1.35, 5.1.34, 5.1.33, 5.1.32, 5.1.31, 5.1.30, 5.1.29, 5.1.28, 5.1.27, 5.1.26, 5.1.25, 5.1.24, 5.1.23, 5.1.22, 5.1.21, 5.1.20, 5.1.19, 5.1.18 ...
https://downloads.mysql.com
MySQL ConnectorJ 5.1.37 has been released
2015年10月22日 — I'm pleased to announce: MySQL Connector/J 5.1.37 Maintenance Release is now available. MySQL Connector/J can be downloaded from the ...
https://dev.mysql.com
mysql-connector-java » 5.1.37
2015年10月6日 — This driver supports auto-registration with the Driver Manager, standardized validity checks, categorized SQLExceptions, support for large ...
https://mvnrepository.com
MySQL資料連結
2023年1月10日 — ... Mysql 資料庫驅動為5.1.37 版本為獲得更好的取數效能。(5.1.37 版本的驅動不支援V5.1、V8.0 的資料庫)mysql-connector-java-5.1.37.jar. 使用者若 ...
https://help.fanruan.com
[Bug]3.7.2版本不支持连接mysql 5.1.37-community #11919
2023年10月19日 — @2023fan 5.1 版本的MySQL 不支持,最低版本支持到5.7。
https://github.com
下载MySQL 5.1.37 Windows 版
下载MySQL 5.1.37 Windows 版。快速下载最新免费软件!马上单击.
https://filehippo.com
|